⚠️ Note: This feature is available starting from version 15.6.0 of OntimizeWeb. Make sure your project is using this version or higher to take advantage of this functionality.
In addition to Ontimize-based services, OntimizeWeb allows integration with third-party APIs using the JSON:API specification. This allows standardized communication with external systems and services.
Overview
To use JSON:API, OntimizeWeb provides an BaseDataService, an abstract class that allows developers to implement full CRUD operations aligned with JSON:API conventions.
OntimizeWeb is compatible with servers that implement the JSON:API specification for standardized data exchange. By default, OntimizeWeb doesnot use the JSONAPIService to perform CRUD operations according to this standard. If needed, you can also configure the application to use services that extend JSONAPIService by setting the serviceType attribute in the application configuration or in the component’s service-type input or provides this service using the O_DATA_SERVICE injection token in your application module.
JSON:API services methods
Service JSONAPIService has the same methods for configuring and sending request to the server. This methods are the following:
/* Configuration methods */
getDefaultServiceConfiguration(serviceName?: string): Object;
configureService(config: any): void;
buildHeaders():void;
/* CRUD methods */
queryById(queryParams: JSONAPIQueryParameter): Observable<JSONAPIResponse> ;
query(queryParams: JSONAPIQueryParameter): Observable<JSONAPIResponse>;
insert(attributes: object, type: string): Observable<JSONAPIResponse>;
update(id: string | object, attributes: object, type: string): Observable<JSONAPIResponse>;
delete(id: object): Observable<JSONAPIResponse>;
/**
* Successful response parsers, there is one parser for each CRUD method which calls to the common parser.
* User can overwrite the chosen methods parsers or the common parser
*/
protected parseSuccessfulResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseSuccessfulQueryResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseSuccessfulAdvancedQueryResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseSuccessfulInsertResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseSuccessfulUpdateResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseSuccessfulDeleteResponse(resp: JSONAPIResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
/**
* Unsuccessful response parsers, there is one parser for each CRUD method which calls to the common parser.
* User can overwrite the chosen methods parsers or the common parser
*/
protected parseUnsuccessfulResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseUnsuccessfulQueryResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseUnsuccessfulAdvancedQueryResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseUnsuccessfulInsertResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseUnsuccessfulUpdateResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
protected parseUnsuccessfulDeleteResponse(error: HttpErrorResponse, _innerObserver: Subscriber<JSONAPIResponse>);
/* Authentication methods */
startsession(user: string, password: string): Observable<string | number>
endsession(user: string, sessionId: number): Observable<number>;
hassession(user: string, sessionId: any): Observable<boolean>;
CRUD methods
The CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) methods are used to perform standard JSON:API operations:
Common Query Parameter
All data retrieval methods use a shared parameter type called JSONAPIQueryParameter, which allows filtering, sorting, pagination, and other options when querying resources.
-
JSONAPIQueryParameter: Object used to define filtering and query parameters when requesting resources. If the object is empty, no filters or query options will be applied.id: Unique identifier of the resource.type: Resource type (e.g.,"articles","users").attributes: Object containing resource-specific data fields.relationships: Object that defines relationships between the resource and other JSON:API resources.links: Object containing hyperlinks related to the resource.meta: Object for non-standard meta-information that cannot be expressed as attributes or relationships.page: Object used for pagination parameters (e.g.,number,size).include: Comma-separated list of related resources to include by default.fields: Sparse fieldsets. Limits the attributes and relationships returned per resource type.filter: Object used to apply filtering conditions to the request.Note: JSON:API is agnostic about filtering strategies; server-specific implementations may vary.
sort: Comma-separated list of fields used to sort the results. Use-prefix for descending order (e.g.,-created,title).
Method Definitions
- query: performs a request to get data from the server.
- JSONAPIQueryParameter
- advancedQuery: performs a request to get paginated data from the server.
- JSONAPIQueryParameter
- insert: performs a insert operation request to the server.
- attributes: indicates the values to insert.
- type: indicates the type to perform the request.
- update: performs an update operation request to the server.
- ids: indicates the keys values for performing the update.
- attributes: indicates the values to update.
- type: indicates the type to perform the request.
- delete: performs an delete operation request to the server.
- ids: indicates the keys values for performing the deletion.
- type: Resource type.
Server response interface
The standard response from requests made to JSON:API-based servers always follows this structure:
import { BaseResponse } from './base-response.interface';
// Interface for describing errors
interface JSONAPIError {
id?: string; // Unique identifier for this particular error occurrence
status?: string; // HTTP status code applicable to this problem
code?: string; // Application-specific error code
title?: string; // Short, human-readable summary of the problem
detail?: string; // Detailed explanation of the error
source?: {
pointer?: string; // JSON Pointer to the offending part of the document
parameter?: string;
header?: string // a string indicating the name of a single request header which caused the error
};
links?: {
about?: string; // A link that leads to further details about this error
type?: string; // Optional additional links
};
meta?: Record<string, any>; // Optional additional information
}
type JsonApiLinkValue =
| string // Simple URI string
| JsonApiLinkObject // Full link object with metadata
| null;
// Interface for links (can be extended as needed)
interface JSONAPILinks {
[linkName: string]: JsonApiLinkValue; // Dynamic keys: "self", "related", etc.
}
interface JsonApiLinkObject {
href: string; // Required: The actual link URI
meta?: Record<string, any>; // Optional metadata about the link
rel?: string; // Optional: Relation type (if not inferred)
type?: string; // Optional: Media type of the resource
title?: string; // Optional: Human-readable title
}
// Interface for resources
interface JSONAPIResource {
type: string; // Resource type (e.g., "articles", "users")
id: string; // Unique identifier of the resource
attributes?: Record<string, any>; // Attributes of the resource
relationships?: Record<string, any>; // Relationships with other resources (optional)
links?: JSONAPILinks; // Links related to the resource (optional)
meta?: Record<string, any>; // Metadata (optional)
}
// Interface for successful responses
interface JSONAPISuccessfulResponse {
data?: JSONAPIResource | JSONAPIResource[]; // Can be a single resource or a collection
included?: JSONAPIResource[]; // Related resources (optional)
meta?: Record<string, any>; // Metadata (optional)
links?: JSONAPILinks; // Links (optional)
}
// Interface for error responses
interface JSONAPIErrorResponse {
errors?: JSONAPIError[]; // A list of errors
}
// Generic interface that can be used for any API response, either successful or error
export interface JSONAPIResponse extends JSONAPISuccessfulResponse, JSONAPIErrorResponse, BaseResponse { };
You can see an example of a JSON:API service request/response in the images below. You can see the complete response here.
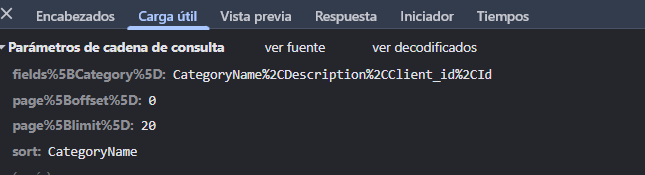
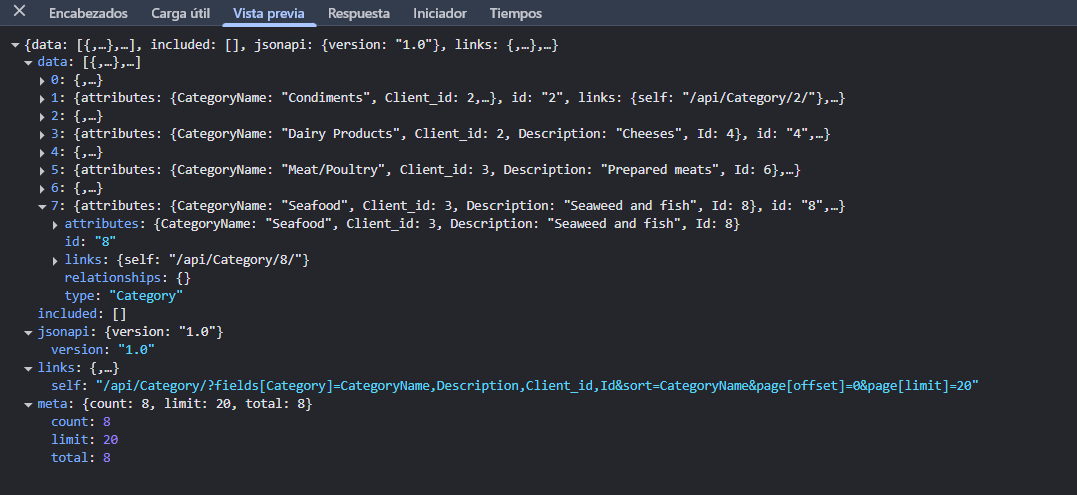
Request arguments interface
In OntimizeWeb, services like JSONAPIService are responsible for constructing the request sent to the backend. To allow flexibility, the framework provides a mechanism to intercept and transform request parameters before they are serialized and sent — this is done using a service adapter.
You can define a custom adapter by implementing the following interface:
export interface IBaseRequestArgument {
parseQueryParameters(params: any): any;
}
Use JSONAPIService in your application
Check the example below about how to configure and use the JSONAPIService for querying data in your application.
protected service: JSONAPIService;
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
this.service = this.injector.get(JSONAPIService);
}
ngOnInit() {
this.configureService();
}
protected configureService() {
// Configure the service using the configuration defined in the `app.services.config.ts` file
const conf = this.service.getDefaultServiceConfiguration('movements');
this.service.configureService(conf);
}
getMovements(data) {
if (data.hasOwnProperty('ACCOUNTID') && this.service !== null) {
const filter = {
'ACCOUNTID': data['ACCOUNTID']
};
const columns = [this.yAxis, this.xAxis, 'DATE_'];
//Note: JSON:API is agnostic about filtering strategies; server-specific implementations may vary.
this.service.query({fields: {movement:columns}, filter:filter}).subscribe(resp => {
if (resp.isSuccessful() === 0) {
// resp.data contains the data retrieved from the server
} else {
alert('Impossible to query data!');
}
});
}
Create and extend a service
⚠️ Note: Rick and Morty API does not support JSON:API specification
Create a new service class that extends to JSONAPIService in OntimizeWeb. In the following example we are creating a service called RickAndMortyService that extends the class JSONAPIService
import { Injectable, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { OntimizeBaseService } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
@Injectable()
export class RickAndMortyService extends JSONAPIService {
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
super(injector);
//Uses Request Arguments to Adapter to prepare params
this.requestArgumentAdapter = this.injector.get(RickAndMortyRequestArgumentsAdapter);
}
public configureService(config: any): void {
super.configureService(config);
this.path = config.path;
}
public configureAdapter() {
//Converts API responses to Ontimize format
this.adapter = this.injector.get(RickAndMortyResponseAdapter);
}
}
Once your service is created you can override the JSON:API CRUD methods and/or define new methods. After that you must decide if the service will be used in the whole application or only in specific components.
Override CRUD methods using a third party API
You can use your service to retrieve or send data to a third party API. The following example shows the service from the previous step consuming the Rick and Morty API for querying different entities. We have overridden the query and advancedQuery methods for making simple and paginated request to the API. Note that you must adapt the API response to the ontimize service response for using the retrieved data with the OntimizeWeb components.
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { Injectable, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { JSONAPIQueryParameter, JSONAPIService, ServiceResponse, Util } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
import { RickAndMortyResponseAdapter } from './rickandmorty-response-adapter';
import { RickAndMortyRequestArgumentsAdapter } from './rickandmorty-request-adapter';
@Injectable()
export class RickAndMortyService extends JSONAPIService {
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
super(injector);
this.requestArgumentAdapter = this.injector.get(RickAndMortyRequestArgumentsAdapter);
}
public configureService(config: any): void {
super.configureService(config);
this.path = config.path;
}
public configureAdapter() {
this.adapter = this.injector.get(RickAndMortyResponseAdapter);
}
query(queryParams: JSONAPIQueryParameter): Observable < ServiceResponse > {
const offset: number = (Util.isDefined(queryParams.page['offset'])) ? queryParams.page['offset'] : 0;
// Calculate page
let page = 0;
if(Util.isDefined(offset)) {
page = Math.trunc(offset / queryParams.page['limit']) + 1;
}
const queryParamsToString = this.toQueryParams(queryParams.filter);
const queryParamsString = ((Util.isDefined(queryParams.filter) && !Util.isObjectEmpty(queryParams.filter)) ? (queryParamsToString + '&') : '?') + 'page=' + page
let url = `${this.urlBase}${this.path}${queryParamsString}`;
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
}
queryById(args_0: any, ...args: any[]): Observable<ServiceResponse> {
let url = `${this.urlBase}${this.path}`;
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
}
insert(args_0: any, ...args: any[]): Observable<ServiceResponse> {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.');
}
update(args_0: any, ...args: any[]): Observable<ServiceResponse> {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.');
}
delete(args_0: any, ...args: any[]): Observable<ServiceResponse> {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.');
}
/**
* Converts a filter object into a query parameter string for a REST request,
* adapted to the Rick and Morty API.
*
* This method removes wildcard characters like `%` (e.g., from SQL-like search patterns),
* and properly encodes keys and values for safe use in a URL.
*
* It also filters out null, undefined, or empty values.
*
* @param obj An object with key-value pairs representing the search filters (e.g., { name: '%rick%' })
* @returns A query string formatted for use in a URL (e.g., "?name=rick")
*
* @example
* toQueryParams({ name: '%morty%', gender: '%male%' });
* // Returns: "?name=morty&gender=male"
*/
public toQueryParams(obj: Record<string, any>): string {
const params = Object.entries(obj)
.filter(([_, value]) => !!value) // remove null/undefined/empty values
.map(([key, value]) => {
const cleanValue = value.replace(/%/g, ''); // remove wildcard %
return `${encodeURIComponent(key)}=${encodeURIComponent(cleanValue)}`;
})
.join('&');
return `?${params}`;
}
}