Services
This section describes the OntimizeWeb services an how to extend them to add or modify its functionality.
Ontimize services
OntimizeWeb services are used for fetching and saving data from servers based on Ontimize. There is two types of Ontimize services depending on the server technology used: OntimizeService and OntimizeEEService. You must indicate which type of service the application will use by configuring the serviceType attribute in the application configuration.
You can also use your own service and adapt its response to OntimizeWeb’s standard response. This will be explained later in this section.
Ontimize services methods
Both services OntimizeService and OntimizeEEService have the same methods for configuring and sending request to the server. This methods are the following:
/* Configuration methods */
getDefaultServiceConfiguration(serviceName?: string): Object;
configureService(config: any): void;
/* CRUD methods */
query(kv?: Object, av?: Array<string>, entity?: string, sqltypes?: Object): Observable<any>;
advancedQuery(kv?: Object, av?: Array<string>, entity?: string, sqltypes?: object,
offset?: number, pagesize?: number, orderby?: Array<object>): Observable<ServiceResponse>
insert(av: Object = {}, entity: string, sqltypes?: object): Observable<ServiceResponse>
update(kv: Object = {}, av: object = {}, entity?: string, sqltypes?: object): Observable<ServiceResponse>
delete(kv: Object = {}, entity?: string, sqltypes?: Object): Observable<ServiceResponse>
/**
* Successful response parsers, there is one parser for each CRUD method which calls to the common parser.
* User can overwrite the chosen methods parsers or the common parser
*/
protected parseSuccessfulResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseSuccessfulQueryResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseSuccessfulAdvancedQueryResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseSuccessfulInsertResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseSuccessfulUpdateResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseSuccessfulDeleteResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
/**
* Unsuccessful response parsers, there is one parser for each CRUD method which calls to the common parser.
* User can overwrite the chosen methods parsers or the common parser
*/
protected parseUnsuccessfulResponse(error: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseUnsuccessfulQueryResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseUnsuccessfulAdvancedQueryResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseUnsuccessfulInsertResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseUnsuccessfulUpdateResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
protected parseUnsuccessfulDeleteResponse(resp: any, _innerObserver: any);
/* Authentication methods */
startsession(user: string, password: string): Observable<any>;
endsession(user: string, sessionId: number): Observable<any>;
redirectLogin?(sessionExpired?: boolean);
CRUD methods
The CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) methods are used to perform standard Ontimize operations:
- query: performs a request to get data from the server.
- kv: indicates the filtering values. An empty object means that no filter will be applied into the request.
- av: indicates the columns that you want to request.
- entity: indicates the entity to perform the request.
- sqltypes: object with the data types for each colum that participates in the request according to Java standard (see SQLType).
- advancedQuery: performs a request to get paginated data from the server.
- kv: indicates the filtering values. An empty object means that no filter will be applied into the request.
- av: indicates the columns that you want to request.
- entity: indicates the entity to perform the request.
- sqltypes: object with the data types for each colum that participates in the request according to Java standard (see SQLType).
- offset: the index of the first item requested in the collection.
- pagesize: the number of items requested.
- orderby: object with the sorting that will be applied to the request result.
- insert: performs a insert operation request to the server.
- av: indicates the values to insert.
- entity: indicates the entity to perform the request.
- sqltypes: object with the data types for each colum that participates in the request according to Java standard (see SQLType).
- update: performs an update operation request to the server.
- kv: indicates the filtering values for performing the update.
- av: indicates the values to update.
- entity: indicates the entity to perform the request.
- sqltypes: object with the data types for each colum that participates in the request according to Java standard (see SQLType).
- delete: performs an delete operation request to the server.
- kv: indicates the filtering values for performing the deletion.
- entity: indicates the entity to perform the request.
- sqltypes: object with the data types for each colum that participates in the request according to Java standard (see SQLType).
Server response interface
The standard response of the requests made to Ontimize based servers always follows the following structure:
{
code: number;
data: Array<Object>;
message: '';
sqlTypes?: Object;
startRecordIndex?: number;
totalQueryRecordsNumber?: number;
}
Where the attributes indicates the following:
- code: indicates the result of the operation: 0 for successful operations, 1 for unsuccessful operations, 3 for session expired.
- data: the data requested.
- message: a message in case the response was not successful.
- sqlTypes: indicates the data type according to Java standard. See SQL Types.
- startRecordIndex: in paginated queries, indicates the position of the first retrieved record in the collection.
- totalQueryRecordsNumber: in paginated queries, indicates the total number of record of the collection.
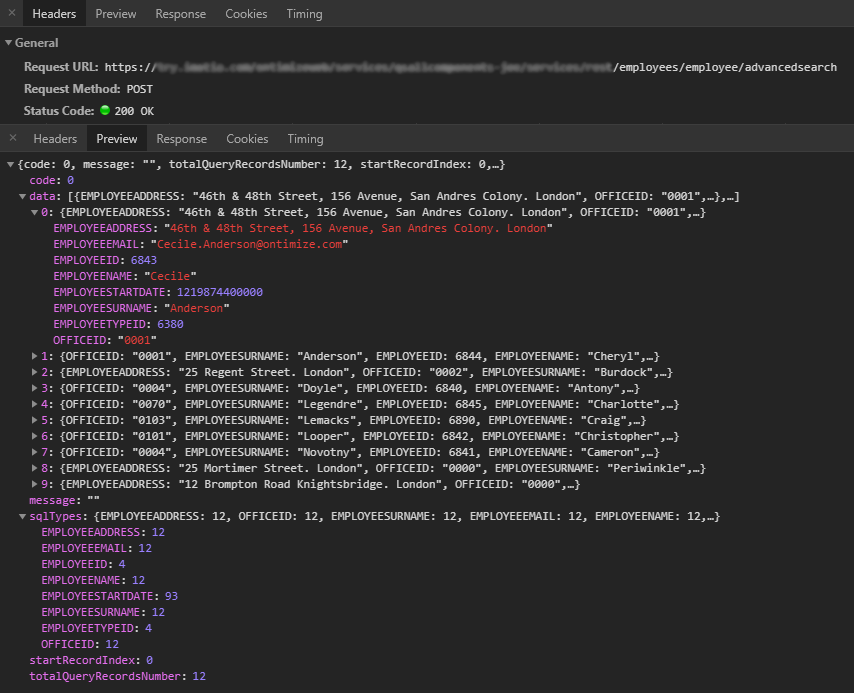
You can see an example of a Ontimize service request response in the image below. You can see the complete response here.
Use OntimizeService in your application
Check the example below about how to configure and use the OntimizeService for querying data in your application.
protected service: OntimizeService;
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
this.service = this.injector.get(OntimizeService);
}
ngOnInit() {
this.configureService();
}
protected configureService() {
// Configure the service using the configuration defined in the `app.services.config.ts` file
const conf = this.service.getDefaultServiceConfiguration('movements');
this.service.configureService(conf);
}
getMovements(data) {
if (data.hasOwnProperty('ACCOUNTID') && this.service !== null) {
const filter = {
'ACCOUNTID': data['ACCOUNTID']
};
const columns = [this.yAxis, this.xAxis, 'DATE_'];
this.service.query(filter, columns, 'movement').subscribe(resp => {
if (resp.code === 0) {
// resp.data contains the data retrieved from the server
} else {
alert('Impossible to query data!');
}
});
}
Extending Ontimize Web services
You can override or extend the functionality of the services defined in OntimizeWeb. You should know that some services are used internally and they cannot be extended. The prepared-to-extend services are the following:
| Service | Injection token | Description |
|---|---|---|
OntimizeService and OntimizeEEService |
O_DATA_SERVICE |
Service used for making CRUD operation and authentication |
OTranslateService |
O_TRANSLATE_SERVICE |
Service for translating the information shown in the application |
OntimizeFileService |
O_FILE_SERVICE |
Service for uploading files, used by the o-file-input component |
OntimizeExportService and OntimizeExportService3X |
O_EXPORT_SERVICE |
Service used by the o-table component for exporting its data |
OntimizePermissionsService and OntimizeEEPermissionsService |
O_PERMISSION_SERVICE |
Service used for loading the application permissions |
AuthService |
O_AUTH_SERVICE |
Service used for authentication (since ontimize-web-ngx@8.3.0) |
OReportService |
O_REPORT_SERVICE |
Service used to generate reports (since ontimize-web-ngx@8.7.0) |
OntimizeExportDataProviderService and OntimizeExportDataProviderService3X |
O_EXPORT_DATA_SERVICE |
Service used to provide data and styles to table exports (since ontimize-web-ngx@8.8.0) |
For extending a service you should create your own service that extends a service from OntimizeWeb and provide it in your application using the corresponding injection token from the table above.
Create and extend a service
Create a new service class that extends a service from OntimizeWeb. In the following example we are creating a service called StarWarsService that extends the class OntimizeBaseService (OntimizeBaseService is the super class for different services in OntimizeWeb).
import { Injectable, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { OntimizeBaseService } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
@Injectable()
export class StarWarsService extends OntimizeBaseService {
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
super(injector);
}
}
Once your service is created you can override the Ontimize CRUD methods and/or define new methods. After that you must decide if the service will be used in the whole application or only in specific components.
Override CRUD methods using a third party API
You can use your service to retrieve or send data to a third party API. The following example shows the service from the previous step consuming the Star Wars API for querying different entities. We have overridden the query and advancedQuery methods for making simple and paginated request to the API. Note that you must adapt the API response to the ontimize service response for using the retrieved data with the OntimizeWeb components.
import { Injectable, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, OntimizeBaseService, Util } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
@Injectable()
export class StarWarsService extends OntimizeBaseService {
constructor(protected injector: Injector) {
super(injector);
}
public query(kv?: Object, av?: Array<string>, entity?: string, sqltypes?: Object): Observable<any> {
const url = 'https://swapi.dev/api/' + entity + '/?format=json';
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
}
public advancedQuery(kv?: Object, av?: Array<string>, entity?: string, sqltypes?: Object, offset?: number, pagesize?: number, orderby?: Array<Object>): Observable<any> {
offset = (Util.isDefined(offset)) ? offset : this.offset;
// Calculate page
let page = 0;
if (Util.isDefined(offset)) {
page = Math.trunc(offset / 10) + 1;
}
let url = 'https://swapi.dev/api/' + entity + '/?format=json' + '&page=' + page;
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
}
}
doRequest method
This doRequest method is used to retrieve data from a URL. You can use this method with parameters to configurate the request.
You can check the options available in this example:
export type ServiceRequestParam = {
method: 'GET' | 'POST' | 'PUT' | 'DELETE',
url: string,
body?: any,
options?: HttpRequestOptions,
successCallback?: (resp: ServiceResponse, observer: Subscriber<ServiceResponse>) => void,
errorCallBack?: (resp: ServiceResponse, observer: Subscriber<ServiceResponse>) => void
};
// this.doRequest(ServiceRequestParam)
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
NOTE: In most cases the third party API won’t offer the same response as OntimizeWeb components need so you have to adapt the response.
Define your own CRUD methods
All the OntimizeWeb components that use services for retrieving data have the attributes query-method, paginated-query-method, insert-method, update-method and deleted-method. The purpose of these attributes is allowing the component to use your own CRUD methods defined in your service. With this you can define, for example, as many query methods as you want.
In the example below we have defined the getSkywalker method that retrieves information from the API.
import { Injectable, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, OntimizeBaseService, Util } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
@Injectable()
export class StarWarsService extends OntimizeBaseService {
...
public getSkywalker(): Observable<any> {
const url = 'https://swapi.dev/api/people/1/?format=json';
return this.doRequest({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
options: {} // This overrides the default http headers. Remove it if you are using an ontimize based API in the backend
});
}
}
Now you can configure a component from OntimizeWeb to use your method. Read more about this in the section Use your service in a specific component.
NOTE: In most cases the third party API won’t offer the same response as OntimizeWeb components need so you have to addapt the response.
Adapt your service response
This section describes how to adapt the response of a third party API in order to use it with OntimizeWeb components.
First of all, you have to implement an adapter. An adapter is a service that implements the interface ServiceResponseAdapter<BaseServiceResponse> that contains the method adapt(resp: HttpResponse<T>): BaseServiceResponse, this method receives the response from the API and returns an instance of BaseServiceResponse that is recognized by OntimizeWeb components.
import { HttpResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { BaseServiceResponse, OntimizeServiceResponse, ServiceResponseAdapter, Util } from 'ontimize-web-ngx';
import { StarWarsResponse } from './star-wars-response.type';
@Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' })
export class StarWarsResponseAdapter implements ServiceResponseAdapter<BaseServiceResponse> {
adapt(resp: HttpResponse<StarWarsResponse>): BaseServiceResponse {
let code = 1;
let data = [];
let message = '';
let sqlTypes = {};
let startRecordIndex = 0;
let totalQueryRecordsNumber = 0;
// Adapt the data received from the service
if (resp.body) {
code = 0;
if (resp.body.results) {
data = resp.body.results;
startRecordIndex = Util.isDefined(resp.body.previous) ? (10 * (this.getPage(resp.body.previous, resp.body.next) - 1)) + 1 : 0;
totalQueryRecordsNumber = resp.body.count;
} else {
data = [resp.body];
}
}
// Create Ontimize service response with the data adapted
return new OntimizeServiceResponse(code, data, message, sqlTypes, startRecordIndex, totalQueryRecordsNumber);
}
...
}
This is the StarWarsResponse referred above.
export interface StarWarsResponse {
count: number;
next: string;
previous: string;
results: any[];
}
The second step is to make your service use the adapter. Your service should extend the class OntimizeBaseService or any of its child classes (OntimizeService, OntimizeEEService, OntimizeExportService and OntimizeFileService). This class implements the method configureAdapter that has to be overwritten in order to provide your adapter.
import { StarWarsResponseAdapter } from './star-wars-response-adapter';
@Injectable()
export class StarWarsService extends OntimizeBaseService {
...
public configureAdapter() {
this.adapter = this.injector.get(StarWarsResponseAdapter);
}
...
}
After this, your adapter will be called every time your service receives a response.
You can also extend the BaseServiceResponse according to your needs. Just remember to respect this three methods that are used internally in OntimizeWeb:
- isSuccessful()
- isFailed()
- isUnauthorized()
Use your service in the whole application
In case you want to use your service in the whole application, you have to provide it in you application module using the corresponding injection token.
@NgModule({
...
providers: [
...
{ provide: O_DATA_SERVICE, useValue: StarWarsService }
]
})
export class AppModule { }
At this point every OntimizeWeb component will use your recently created StarWarsService service for communicating with the backend.
NOTE:
OntimizeService,OntimizeEEService,OntimizeExportService,OntimizePermissionsServiceandOntimizeEEPermissionsServicecan be extended and used in the whole application by indicating the class in the application configuration. There is one attribute for each type of service.
Use your service in a specific component
If you want to use your service in a specific component instead of using it in the whole application, you have to create a provide method that returns a new instance of your service and add a provider to your module indicating the factory method like in the example below.
import { StarWarsService } from '../../shared/star-wars.service';
@NgModule({
...
providers: [{
provide: 'starWars',
useValue: StarWarsService
}]
})
export class MyModule { }
Once the service is included in the providers of your module, it will be created an instance of the service for each component. For this, configure the service-type attribute in the component with the value of the provide attribute indicated in the previous step. Check the example below.
<o-table attr="starships" entity="starships" columns="name;model;manufacturer;starship_class;crew;passengers"
visible-columns="name;model;manufacturer;starship_class;passengers" pageable="yes" quick-filter="no" insert-button="no" fxFlex
service-type="starWars">
...
</o-table>
Define your own successful/unsuccessful request callback methods
OntimizeWeb defines a successful and unsuccessful request callbacks for each CRUD method, this methods are called when the service receives the response from the API. You can override this methods in order to modify its behaviour. This methods are: parseSuccessfulMETHODResponse and parseUnsuccessfulMETHODResponse where METHOD is query, advancedQuery, update, insert or delete.
Both services OntimizeService and OntimizeEEService also have a generic succesful and unsuccessful request callback which are parseSuccessfulResponse and parseUnsuccessfulResponse. This callbacks are called from the previous explained CRUD method callbacks so user can choose whether to override a particular or the generic method.